-
Effective Use of Steam and Steam Traps
-
Examples of Condensate Recovery
-
Types of condensate recovery can be broadly divided into open systems and closed systems.
In an open system, the recovered condensate is collected in an open recovery tank under atmospheric pressure. Therefore, the condensate temperature is 100 ℃ or less and some of the heat energy is released to the atmosphere as flash steam. On the other hand, a closed system is a pressurized recovery, and is suitable for efficiently recovering high temperature condensate energy.
However, the cost of developing recovery system is higher in the latter case. Thus, it is necessary to choose the type of condensate recovery system based on a comprehensive consideration of the purpose of recovery, the scale of recovery, and other factors. Several examples of condensate recovery piping are shown below (a check valve is required before the boiler, although it is omitted in each figure).
-
Basic recovery to water supply tank
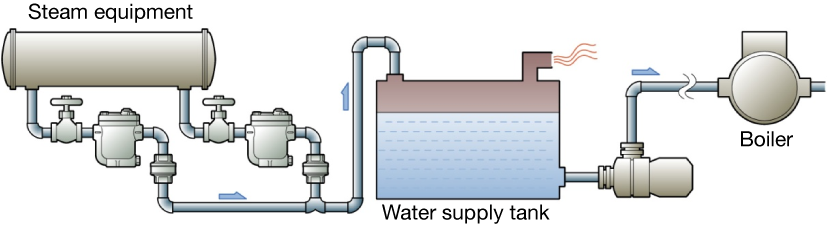
Figure 5.3 Open system
Condensate is recovered to water supply tank by primary side pressure through the steam trap.
-
Recovery using a line pump
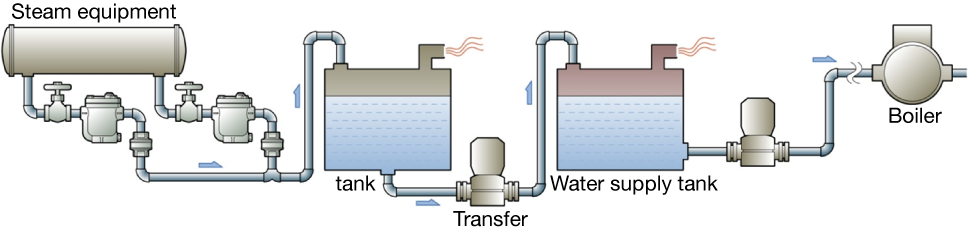
Figure 5.4 Open system using a line pump
If condensate could not be recovered to water supply by the primary side pressure of steam trap, a relay line pump needs to be installed before water supply tank. A cushion tank is installed to temporarily store the condensate.
-
Recovery using condensate recovery pump
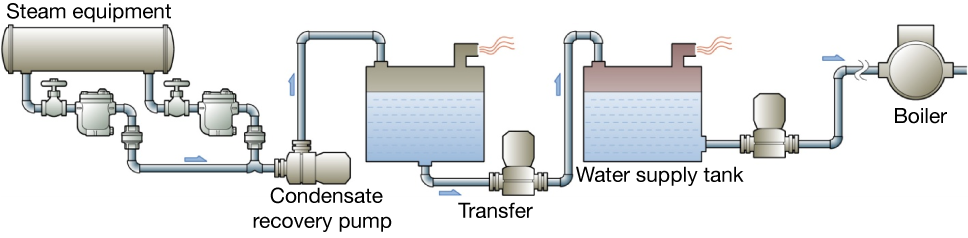
Figure 5.5 Open system using condensate recovery pump
It is necessary to install a condensate recovery pump for providing the power to withdraw the condensate when pressure from the steam trap is low.
-
Pressure recovery system to the boiler
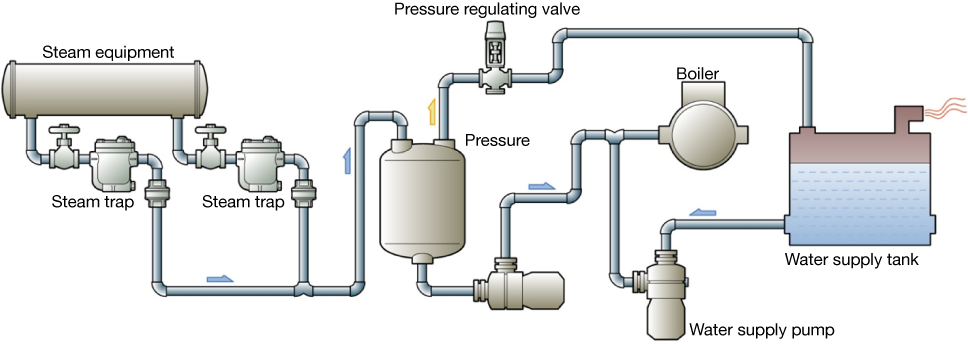
Figure 5.6 Closed system
The recovered condensate is led to the boiler directly via a recovery pump from the pressure tank. When the primary side of the pump receives excessive pressure, it is necessary to use a pressure regulating valve to release pressure to the water supply tank to protect the pump.
-
Effective use of flash steam
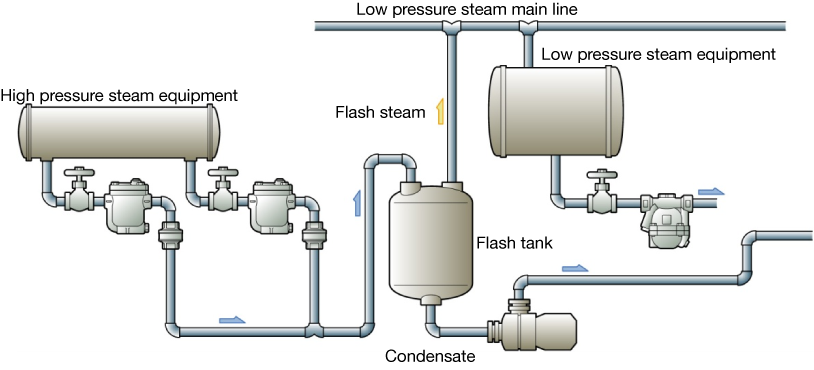
Figure 5.7 Use of flash steam and condensate recovery
The recovered condensate is led to a flash tank for re-evaporation and the flash steam is reused in a low pressure steam line. Non evaporated condensate is recovered for other purposes.
-
Reuse of impure steam
As mentioned previously, condensate is water that has been treated and distilled to near pure water. However, some condensate may get contaminated in the process of steam consumption by mixing with impure substance.
For instance, chemical leakage occurs due to deterioration of chemical reaction equipment, or corrosion and rust may be mixed into the line or the equipment when the system is deactivated after a long-time system shutdown. Water contaminated in this way is not suitable for reusing as water to be supplied to the boiler, but can be used for heat transfer or other production facilities.